Plastics have become an integral part of modern life due to their versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness. However, the widespread use of traditional plastics has led to significant environmental challenges. Globally, millions of tons of plastic waste are generated annually, much of which ends up in oceans, harming marine life and disrupting ecosystems. Landfills are overflowing with plastic debris that can persist for centuries, contributing to soil and water contamination.
Traditional plastics are primarily derived from petrochemicals and are designed for durability. While this durability is beneficial for product longevity, it poses a significant problem when these products are discarded. Most conventional plastics do not readily decompose in natural environments, leading to accumulation and persistent pollution. Over time, these plastics break down into microplastics, which infiltrate food chains and pose health risks to wildlife and humans alike.
In response to the escalating plastic pollution crisis, biodegradable plastics have emerged as a promising alternative. These materials are designed to break down more rapidly under specific environmental conditions, potentially reducing the long-term impact of plastic waste. By integrating biodegradable plastics into various applications, we can aim to mitigate some of the environmental challenges posed by traditional plastics.

What Is Biodegradable Plastic
Biodegradability refers to the ability of a material to be broken down by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, into natural substances like water, carbon dioxide, and biomass. This process occurs over time and depends on environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of microorganisms.
Type of Biodegradable Plastic
Starch-Based Biodegradable Plastics
Starch-based plastics are derived from natural starches obtained from crops like corn, potatoes, and wheat. These materials are often blended with other biodegradable polymers to enhance their mechanical properties. They are commonly used in packaging, agricultural films, and disposable items.
Polylactic Acid (PLA) Plastics
PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic made from fermented plant sugars, typically sourced from corn starch or sugarcane. It is widely used in food packaging, disposable tableware, and biomedical applications due to its clarity, strength, and compostability.
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)
PHAs are a family of biodegradable polyesters produced by bacterial fermentation of sugars or lipids. They are known for their biocompatibility and are used in medical applications, packaging, and agricultural products.
Cellulose-Based Plastics
Derived from natural cellulose found in plants, these plastics are modified to achieve desired properties. They are used in film production, coatings, and as additives to enhance biodegradability in other plastic formulations.
Other Emerging Types
- Polybutylene Succinate (PBS): A biodegradable polyester with applications in packaging and agricultural films.
- Polycaprolactone (PCL): A synthetic aliphatic polyester used in medical devices and as a blending agent to enhance the biodegradability of other polymers.

What Is Biodegradable Plastic Bags Made Of
- Polylactic Acid (PLA): Derived from fermented plant sugars, such as those from corn starch or sugarcane, PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic. It is widely used in food packaging, disposable tableware, and biomedical applications due to its clarity, strength, and compostability.
- Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA): PHAs are a family of biodegradable polyesters produced by bacterial fermentation of sugars or lipids. They are known for their biocompatibility and are used in medical applications, packaging, and agricultural products.
- Starch-Based Plastics: These are made by blending starch (commonly from corn, potatoes, or wheat) with other biodegradable polymers to enhance their mechanical properties. They are often used in packaging, agricultural films, and disposable items.
- Cellulose-Based Plastics: Derived from natural cellulose found in plants, these plastics are modified to achieve desired properties and are used in film production, coatings, and as additives to enhance biodegradability in other plastic formulations.

Advantages of Biodegradable Plastics
Environmental Friendliness:
Biodegradable plastics are made from natural materials such as cornstarch, vegetable fats, and oils, which are renewable resources. Microorganisms can break these materials down into carbon dioxide, water, and biomass, which the environment can reuse. Unlike traditional plastics, biodegradable plastics do not release harmful chemicals into the atmosphere, making them a more sustainable option.
Reduction of Waste in Landfills:
Traditional plastics take hundreds of years to decompose, occupying valuable space in landfills. Biodegradable plastics decompose much faster, reducing the amount of space needed in landfills and potentially decreasing the need for new landfill sites.
Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
The production of biodegradable plastics often requires less energy compared to traditional plastics. For instance, manufacturing corn-based polymers requires 65% less energy than producing similar polymers from petroleum. This reduction in energy consumption leads to fewer greenhouse gas emissions during production.
Non-Toxicity:
Traditional plastics are made using harmful by-products and chemicals, which can be a threat to the environment and life. They are likely to emit these harmful substances during the breakdown process. Biodegradable plastics, on the other hand, are manufactured using natural materials and do not release harmful chemicals into the environment, making them a safer alternative.
Versatility:
Biodegradable plastics are versatile and can be used in various applications, including packaging materials, disposable cutlery, and even medical implants. They can be molded into different shapes and sizes, making them highly adaptable to various needs.
Promotion of a Circular Economy:
Biodegradable plastics can promote a circular economy by reducing waste and creating a closed-loop system. In a circular economy, waste is minimized, and resources are reused and recycled. Biodegradable plastics can help to create a closed-loop system by breaking them down into natural components that can be used to make new products. This reduces the amount of waste in landfills and promotes a more sustainable system.

Biodegradable Production Processes and Raw Materials
Renewable Resources as Raw Materials
Biodegradable plastics are often produced from renewable resources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Common feedstocks include:
- Corn Starch: Used in the production of PLA and starch-based plastics.
- Sugarcane: Fermented to produce lactic acid for PLA synthesis.
- Vegetable Oils: Utilized in the production of certain PHAs.
Environmental Impact of the Production Process
The production of biodegradable plastics can have a lower environmental footprint compared to traditional plastics, especially when using renewable resources. However, factors such as land use for crop cultivation, water consumption, and energy use must be considered to ensure overall sustainability.
Comparison with Traditional Plastic Production
While biodegradable plastics offer environmental benefits, their production can be more resource-intensive and costly. Advancements in technology and economies of scale are expected to reduce these costs over time, making biodegradable options more competitive with traditional plastics.
Applications of Biodegradable of Plastic
Applications in the Packaging Industry
- Food Packaging: Containers, wraps, and films that can be composted after use.
- Shopping Bags: Compostable bags that reduce plastic waste.
- Disposable Tableware: Plates, cups, and cutlery made from materials like PLA.
Applications in Agriculture
- Mulch Films: Films that degrade in soil, eliminating the need for removal and disposal.
- Plant Pots and Seed Trays: Containers that can be planted directly into the ground, reducing transplant shock and waste.
Biodegradable Materials in the Medical Industry
- Sutures: Absorbable stitches that eliminate the need for removal.
- Drug Delivery Systems: Implants that release medication over time and degrade safely in the body.
- Tissue Engineering: Scaffolds that support cell growth and degrade as new tissue forms.
Applications in Everyday Consumer Products
- Disposable Items: Cutlery, straws, and plates used in food service.
- Personal Care Products: Packaging for cosmetics and hygiene products.
- Textiles: Fibers used in clothing and non-woven fabrics.
How Consumers Can Support the Use of Biodegradable Plastics
Stay Informed: Understand the differences between biodegradable, compostable, and bio-based plastics.
Proper Disposal: Follow local guidelines for disposing of biodegradable plastics to ensure they are processed correctly.
Advocate for Infrastructure: Support initiatives and policies aimed at developing the necessary infrastructure for managing biodegradable plastics.
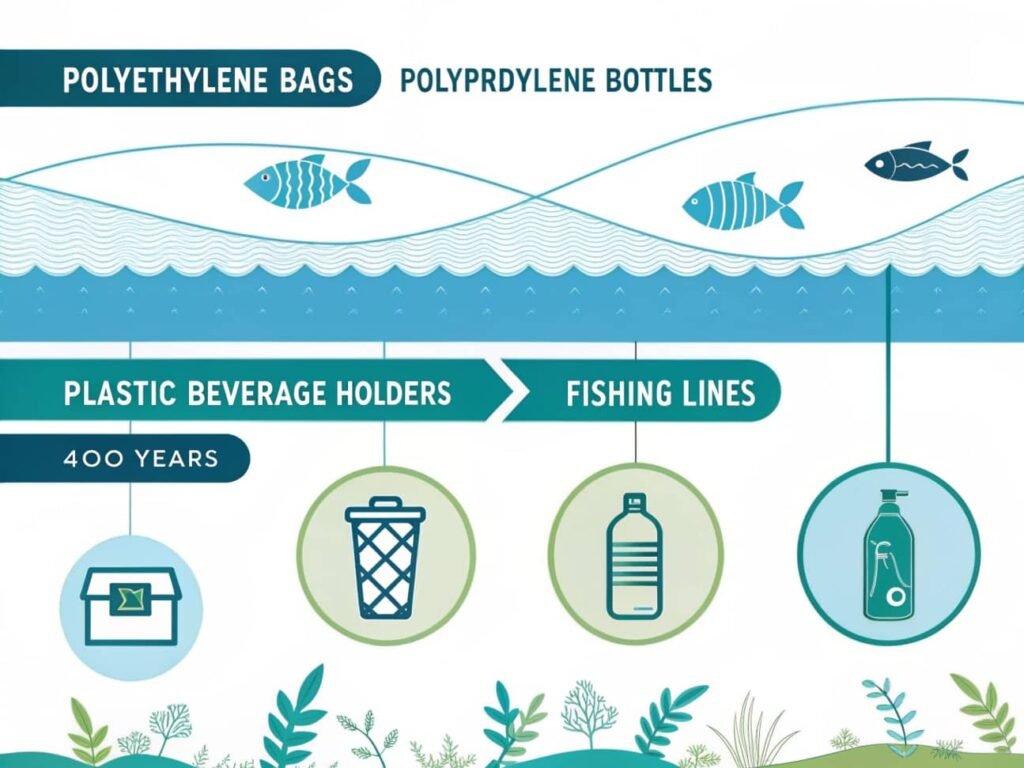
How Long Does It Take for Plastic to Biodegrade
Traditional plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are highly resistant to natural degradation processes. In marine environments, it's estimated that a plastic beverage holder can take up to 400 years to decompose, while fishing lines may persist for 600 years.
Biodegradable Plastics:
Biodegradable plastics are engineered to break down more quickly than conventional plastics. However, their degradation rates can vary:
Standard Biodegradable Plastics: Under optimal conditions, such as industrial composting facilities with controlled temperature and humidity, these plastics can decompose within 6 to 18 months. In less ideal environments, like landfills or natural settings, the degradation process can extend to several years.
Compostable Plastics: Designed to break down in composting environments, some compostable bags have been observed to disappear in marine settings within three months. However, when buried in soil, they can still be present after 27 months.
Advanced Biodegradable Plastics: Innovations have led to plastics embedded with specific enzymes that, when exposed to heat and water, can degrade entirely within a few weeks. For instance, certain modified plastics have been shown to break down completely in standard compost within two weeks.
Environmental Factors:
Temperature and Humidity: Higher temperatures and moisture levels can accelerate the breakdown of biodegradable plastics.
Microbial Activity: The presence and activity of microorganisms play a crucial role in the decomposition process.
Exposure to Sunlight: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation can cause photodegradation, leading to the fragmentation of plastics into microplastics, which persist in the environment.
| Type of Biodegradable Plastic | Degradation Rate in Optimal Conditions | Degradation Rate in Less Ideal Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Biodegradable Plastics | 6 to 18 months in industrial composting facilities with controlled temperature and humidity. | Several years in landfills or natural settings. |
| Compostable Plastics | Some compostable bags disappear in marine settings within three months. | Can remain intact in soil for over 27 months. |
| Advanced Biodegradable Plastics | Certain modified plastics degrade completely in standard compost within two weeks. | Degradation rates in less controlled environments may vary and require further study. |
Conclusion
Biodegradable plastics present a promising avenue for mitigating plastic pollution. When designed and managed appropriately, they can reduce the persistence of plastic waste in the environment. However, they are not a panacea and should be part of a broader strategy that includes reducing plastic consumption, enhancing recycling efforts, and developing alternative materials.



