As concerns about plastic waste continue to grow, more businesses and consumers are looking for alternatives to conventional plastics. One of the most discussed options is biodegradable plastic.
However, the term is often misunderstood. Many people assume that all biodegradable plastics break down quickly in nature or are automatically compostable. In reality, biodegradable plastic is a broad category that includes different materials, different degradation conditions, and different environmental outcomes.
This guide explains what biodegradable plastic means, how it breaks down, the main material types, and how it differs from compostable plastic.
For a broader comparison of sustainable material options, see our guide to bioplastics vs plastics.

What Is Biodegradable Plastic?
Biodegradable plastic refers to plastic materials that can be broken down by microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and algae into simpler natural substances under specific conditions.
Depending on the material and environment, the final breakdown products may include:
- carbon dioxide
- water
- methane
- biomass
- mineral salts
The key point is that biodegradation depends on time, temperature, humidity, oxygen level, and microbial activity. A plastic labeled biodegradable does not necessarily break down quickly in every environment.
How Does Biodegradable Plastic Break Down?
Biodegradable plastic degrades through microbial activity. When exposed to suitable environmental conditions, microorganisms consume the polymer chains and convert them into smaller molecules.
The degradation process usually depends on several factors:
- temperature
- moisture
- oxygen availability
- microbial population
- material thickness and formulation
Some biodegradable plastics break down mainly in industrial composting facilities, while others may degrade in soil or other environments more slowly.
This is why biodegradable plastic should not be treated as a guarantee of rapid decomposition in open nature.
Types of Biodegradable Plastic
Biodegradable plastics can be divided into two main groups based on raw material source.
1. Bio-based biodegradable plastics
These materials are derived partly or fully from renewable biomass such as corn, cassava, sugarcane, or plant oils.
Common examples include:
- PLA (polylactic acid)
- PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoate)
- starch-based plastics
These materials are often used in compostable packaging, food service products, and biodegradable films.
Related reading:
2. Petrochemical-based biodegradable plastics
These materials are synthesized from fossil-based chemical feedstocks but are still designed to biodegrade under suitable conditions.
Common examples include:
- PBAT
- PBS
- PCL
These materials are often blended with bio-based polymers to improve flexibility, toughness, and processing performance.
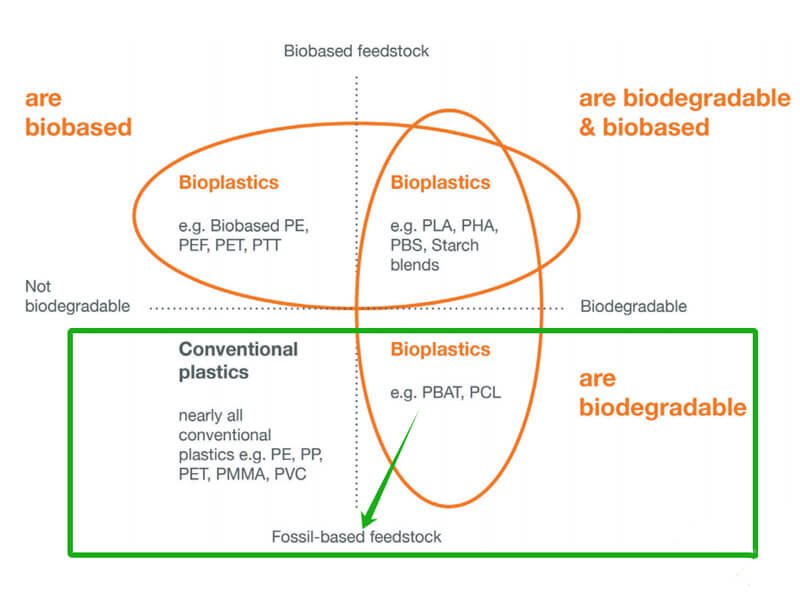
An important point is that bio-based and biodegradable are not the same thing. A plastic can be fossil-based and biodegradable, or bio-based and not biodegradable.
Common Biodegradable Plastic Materials
Several biodegradable materials are widely used in packaging and industrial applications.
PLA
PLA is a bio-based plastic usually made from fermented plant sugars. It is commonly used in food packaging, disposable products, and compostable films. PLA usually requires industrial composting conditions to break down efficiently.
PBAT
PBAT is a synthetic biodegradable polymer known for its flexibility. It is often used in compostable bags and packaging films, especially when blended with PLA or starch.
PHA
PHA is produced through microbial fermentation. It is one of the most promising biodegradable plastics because it can break down in a wider range of environments than many other bioplastics.
Starch-based plastics
These materials use plant starch as a major component and are usually blended with other biodegradable polymers to improve strength and moisture resistance.
Biodegradable Plastic vs Compostable Plastic
Biodegradable plastic and compostable plastic are related, but they are not identical.
| Aspect | Biodegradable Plastic | Compostable Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Can be broken down by microorganisms over time | Must break down under composting conditions within a defined timeframe |
| Time requirement | Not always clearly defined | Usually defined by certification standards |
| End result | Simpler natural substances | Must also leave no harmful residues and support compost quality |
| Certification | May or may not be certified | Usually certified under standards such as ASTM D6400 or EN 13432 |
| Typical use | Broad range of applications | Packaging and products intended for composting systems |
In simple terms, all compostable plastics are biodegradable, but not all biodegradable plastics are compostable.
For certification requirements, see:

Are Biodegradable Plastics Really Environmentally Friendly?
Biodegradable plastics can offer environmental benefits, but only when they are used appropriately and disposed of through suitable systems.
They may provide advantages such as:
- reduced long-term persistence compared with conventional plastics
- lower dependence on fossil fuels in some cases
- compatibility with organic waste systems for certain products
- support for compostable packaging applications
However, biodegradable plastics are not automatically the best solution in every situation.
Their real environmental value depends on:
- the specific material
- whether proper disposal infrastructure exists
- whether the product is certified compostable
- how consumers actually discard the product
If biodegradable plastics are littered, landfilled, or mixed into the wrong waste stream, their environmental benefits may be reduced.
Advantages of Biodegradable Plastics
Reduced plastic persistence
Some biodegradable plastics can break down faster than conventional plastics under appropriate conditions.
More sustainable feedstock options
Many biodegradable plastics use renewable resources such as corn starch, sugarcane, or plant oils.
Useful for compostable packaging
Biodegradable plastics are widely used in food waste liners, compostable bags, and other applications linked to organic waste collection.
Broad design flexibility
They can be processed into films, bags, molded products, and specialty packaging.

Limitations of Biodegradable Plastics
Not all degrade in nature
Many biodegradable plastics still need controlled environments such as industrial composting facilities.
Consumer confusion
Terms such as biodegradable, compostable, bio-based, and oxo-degradable are often misunderstood.
Higher material cost
Some biodegradable plastics remain more expensive than conventional plastics.
Infrastructure dependency
Without suitable composting or waste treatment systems, environmental benefits may not be fully realized.
Bioplastics, Bio-based Plastics, Biodegradable Plastics and Oxo-degradable Plastics
These terms are often confused, but they describe different concepts.
| Category | Main Meaning | Biodegradable? | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bioplastics | Plastic that is bio-based, biodegradable, or both | Sometimes | PLA, PHA |
| Bio-based plastics | Plastic made partly from renewable biomass | Not always | Bio-PE, Bio-PET |
| Biodegradable plastics | Plastic designed to be broken down by microorganisms | Yes, under suitable conditions | PLA, PBAT, PHA |
| Oxo-degradable plastics | Conventional plastics with additives that fragment under oxidation | Not truly biodegradable in the same way | Oxo-PE |
This distinction matters because not every “green plastic” delivers the same environmental performance.
Applications of Biodegradable Plastic
Biodegradable plastics are used in a variety of sectors where disposal, short service life, or sustainability goals are important.
Common applications include:
- compostable garbage bags
- food waste collection liners
- biodegradable courier bags
- agricultural mulch films
- disposable food packaging
- pet waste bags
- certain medical and hygiene products
For commercial packaging applications, see our compostable garbage bags.
What Are the Alternatives to Conventional Plastic?
Biodegradable plastic is one pathway, but not the only one. Common alternative materials include:
- PLA for food packaging and disposable products
- PHA for advanced biodegradable applications
- starch-based plastics for compostable films and bags
- bagasse for molded food containers
- bamboo fiber for household and food service products
- mycelium materials for protective packaging
- seaweed-based materials for emerging flexible packaging concepts
Each alternative has different strengths, costs, and disposal requirements.

Conclusion
Biodegradable plastic is a broad category of materials designed to be broken down by microorganisms under suitable conditions. It includes both bio-based and fossil-based polymers, and it should not be confused with compostable plastic, bio-based plastic, or oxo-degradable plastic.
For packaging buyers and sustainability teams, the most important point is this: a biodegradable plastic is only as effective as its material design, certification status, and end-of-life system.
When selected carefully and used in the right applications, biodegradable plastics can play an important role in reducing plastic waste and supporting more sustainable packaging systems.
FAQ
What is biodegradable plastic?
Biodegradable plastic is a type of plastic that can be broken down by microorganisms into simpler natural substances under specific environmental conditions.
Is biodegradable plastic the same as compostable plastic?
No. Compostable plastic is a more specific category. It must break down within a defined timeframe and meet standards related to compost quality and toxicity.
What are the main types of biodegradable plastic?
The main types include PLA, PBAT, PHA, starch-based plastics, and some other biodegradable polyesters.
Do biodegradable plastics break down naturally?
Some do, but many require specific conditions such as industrial composting, controlled temperature, moisture, and microbial activity.
Are biodegradable plastics better than conventional plastics?
They can be better in some applications, especially for compostable packaging, but their environmental performance depends on material type, certification, and disposal infrastructure.






