With the increase in global environmental awareness, traditional plastics are gradually being abandoned by the market because they are difficult to degrade and have high environmental pollution. Instead, new degradable and environmentally friendly PBAT materials are replacing them.
This article will explain the relevant information about PBAT in detail, hoping to be helpful for users who want to purchase PBAT products.

What is PBAT?
PBAT (full name is polybutylene terephthalate) is a thermoplastic polyester material with excellent biodegradability. It is a semi-crystalline petroleum-based polymer. It has good flexibility and biodegradability.
PBAT is also often blended with PLA (polylactic acid) and PBS (polybutylene succinate) to improve the overall material performance and broaden the scope of application.
PBAT Raw Material Sources
| Component | Typical Source | Renewable? |
|---|---|---|
| Butylene glycol | Petroleum derivatives | No |
| Adipic acid | Corn sugar derivatives | Partial |
| Terephthalic acid | Petroleum/corn hybrid | Partial |
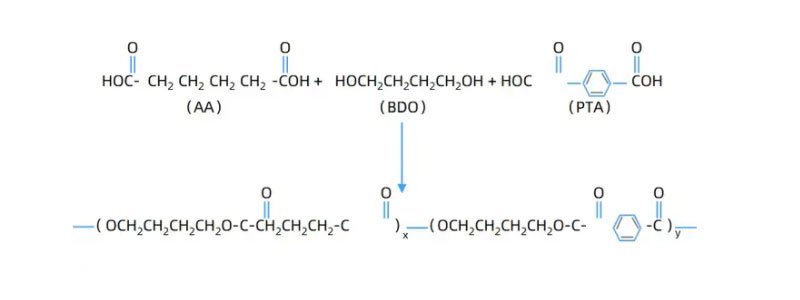
How is PBAT Made ?
Transesterification Method:
PTA (terephthalic acid), DMT (dimethyl terephthalate) and 1,4-butanediol (BDO) are used as raw materials, and PBT prepolymer is obtained through esterification or transesterification reaction under the action of catalyst, and then melt polycondensation reaction is carried out with PBA (polybutylene adipate).
The advantages of this method are narrow molecular weight distribution, less intermediate products, simple reaction equipment, and waste can be reused, but there are problems such as insufficient product quality and performance stability and difficulty in large-scale production.
Direct Esterification Nethod:
PBAT is synthesized by premixing, prepolymerization and final polymerization using adipic acid (AA), BDO and PTA or DMT as raw materials.
Under the condition that organic metal compounds such as zinc, tin and titanium are used as polycondensation catalysts, the raw materials are mixed and esterified, and then the product is obtained by high temperature and high vacuum polycondensation reaction.

Advantages and Disadvantages of PBAT
PBAT advantages
Excellent flexibility and ductility
Unlike the hardness and brittleness of PLA, PBAT is softer and suitable for making packaging products that need to be stretched.
Good processing performance
Applicable to a variety of thermoplastic molding processes such as film blowing, injection molding, and extrusion.
Excellent degradation performance
Meet mainstream environmental certifications, degrade quickly under appropriate conditions, and have no residual toxins.
Strong compatibility with other materials
Can be blended and modified with PLA, starch, PBS, etc. to meet different product requirements.
Disadvantages of PBAT
High raw material cost
Compared with traditional plastics (such as PE), the unit price of PBAT is 3 to 5 times higher.
Slightly poor thermal stability
Easy to degrade at high temperatures, not suitable for long-term high temperature environments or heat sealing scenarios.
Easy to oxidize and age
Easy to oxidize and degrade when exposed to air, requiring appropriate storage conditions.

PBAT Products & Application
PBAT is suitable for a variety of degradable products due to its good flexibility and processing performance.
Degradable garbage bags: With excellent load-bearing capacity and tensile strength, it can be used in a variety of scenarios such as home, commercial, and medical use.
Degradable shopping bags: It can replace traditional PE plastic bags and is suitable for supermarkets, retail stores, and customized environmentally friendly brands.
Express bags/mailing bags: Combined with PBAT and PLA, it can be made into packaging bags with both toughness and degradability.
Agricultural mulch: Good degradability, avoiding the "white pollution" caused by traditional mulch to the soil.
Food packaging film: After certain blending and barrier modification, it can be used for disposable food packaging, take-out packaging, etc.
Disposable items: such as degradable gloves, aprons, straws, cup lids, etc.

PBAT’s Biodegradability and Environmental Benefits
PBAT has gained widespread popularity primarily due to its excellent biodegradability. Under industrial composting conditions (above 50°C, with oxygen and active microbial presence), PBAT can fully decompose within 90 to 180 days, leaving no toxic residues behind.
Comparison with Other Materials:
| Material | Biodegradable | Degradation Environment | Degradation Period | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBAT | ✔ Yes | Industrial composting | 90–180 days | Flexible, high elongation |
| PLA | ✔ Yes | Industrial composting | Around 180 days | Brittle, good moldability |
| PE | ✘ No | Non-degradable | Hundreds of years | Low cost, high pollution |
Certification Standards:
PBAT typically meets the following internationally recognized compostability and environmental standards:
- EN 13432 (European Union)
- ASTM D6400 (United States)
- AS 4736 (Australia)
- OK Compost (TÜV Austria)
- BPI Certified (Biodegradable Products Institute, USA)
These certifications confirm that PBAT can be legally and safely used in compostable packaging products, such as trash bags, shopping bags, and mailers, especially for export to environmentally regulated markets like Europe, North America, and Australia.

PBAT vs. PLA: What’s the Difference?
Both PBAT (Polybutylene Adipate Terephthalate) and PLA (Polylactic Acid) are popular biodegradable plastics, but they differ significantly in terms of properties, origin, processing, and applications.
| Feature | PBAT | PLA |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Petroleum-based synthetic polyester | Bio-based polymer (from corn/starch) |
| Biodegradability | ✅ Yes (fully compostable) | ✅ Yes (fully compostable) |
| Degradation Speed | 90–180 days (industrial composting) | Around 180 days (industrial composting) |
| Flexibility | Very flexible, high elongation at break | Brittle and rigid |
| Melt Processing | Suitable for film blowing, extrusion, etc. | Good for injection molding, thermoforming |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Generally higher |
| Common Applications | Trash bags, shopping bags, mulch film | Straws, food containers, rigid packaging |
| Blending Compatibility | Often blended with PLA, starch | Can be blended with PBAT for flexibility |
| Heat Resistance | Lower heat resistance | Higher than PBAT |
| Certifications | EN13432, ASTM D6400, BPI, OK Compost | EN13432, ASTM D6400, BPI, OK Compost |
Conclusion:
At a time when the concept of sustainable development and environmental protection is deepening, PBAT is gradually becoming the core force of environmentally friendly plastic solutions with its excellent degradation performance, flexibility and processing adaptability. Whether it is a corporate brand or an individual user, choosing PBAT products is a solid step towards a "green future".
FAQs
Is PBAT biodegradable in natural soil?
PBAT is mainly used for industrial composting. In seawater, due to the presence of microorganisms adapted to high-salt environments, PBAT can be completely degraded within about 30-60 days, provided that the temperature is within 25℃±3℃.
Can PBAT be used alone, or must it be blended with other materials?
PBAT can be used alone, especially for flexible packaging. However, it is often blended with PLA or starch to improve strength, rigidity, or cost-efficiency depending on the application.
Is PBAT biodegradable?
Yes, PBAT is a biodegradable polymer. Under appropriate environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and microbial activity, PBAT can be decomposed by microorganisms and eventually converted into carbon dioxide and water.
Is PBAT compostable?
Yes, PBAT is biodegradable under composting conditions.
Under normal climatic conditions, it takes about 5 months for PBAT to be completely degraded in soil.
PBAT is biodegradable under ideal composting conditions, usually about 3-6 months for industrial composting at 50℃-60℃, and about 180 days for home composting.
The degradation rate may be affected by environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and microbial species.
Is PBAT toxic?
PBAT itself is considered non-toxic. However, PBAT may release degradation products such as terephthalic acid (TPA) and 1,4-butanediol during the degradation process. Studies have shown that in soil environments, the short-term accumulation of 1,4-butanediol may pose a certain risk to the ecosystem. Therefore, although PBAT is designed as an environmentally friendly material, the ecological impact of its degradation products still needs further study and evaluation.
Is PBAT food-safe?
Yes, PBAT can be made food-contact safe if processed under hygienic conditions and meets applicable food safety regulations (e.g., FDA, EU food-grade standards).
What’s the shelf life of PBAT products?
PBAT has a typical shelf life of 12–18 months under cool, dry storage. Exposure to heat, light, or oxygen may accelerate degradation.
Are PBAT products recyclable?
No. PBAT is designed to be compostable, not recyclable in the traditional plastic recycling stream. It should be disposed of in industrial composting systems.





