We often see the terms "biodegradable" and "compostable" on many products, but many people confuse the two concepts and mistakenly believe they are the same. However, the difference between biodegradable and compostable is significant.
Everything compostable is biodegradable, but not everything biodegradable is compostable.
- Compostable: The conditions are relatively strict. It must decompose under specific temperature, humidity, and oxygen conditions into nutrient-rich compost that nourishes the soil, leaving no toxic residues. This requires authoritative certification from a professional third-party organization.
- Biodegradable:A vague marketing term. It simply means that it can be decomposed by microorganisms, but the timeframe, conditions, and end product are undefined. It can take hundreds of years, may leave behind toxic plastic particles, and is unregulated.
As a manufacturer with 16 years of experience in compostable bag manufacturing, we'd like to share the key differences between "biodegradable" and "compostable," hoping they will be helpful.

Definition of Biodegradable vs Compostable
What Does Compostable Meaning
Compostable meaning The material breaks down into natural elements such as carbon dioxide, water, and organic matter under specific composting conditions. Composting requires a controlled environment with the right temperature, humidity, and microbial flora. Materials such as PLA and PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates) are often labeled as compostable.
What Does Biodegradable Mean
Biodegradable meaning The process by which a material breaks down naturally over time under the influence of microorganisms. These materials can break down in a variety of environments, but the speed and extent of decomposition depends on factors such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of specific microorganisms. Common biodegradable materials include PLA (polylactic acid) and PBAT (polybutylene adipate-terephthalate).
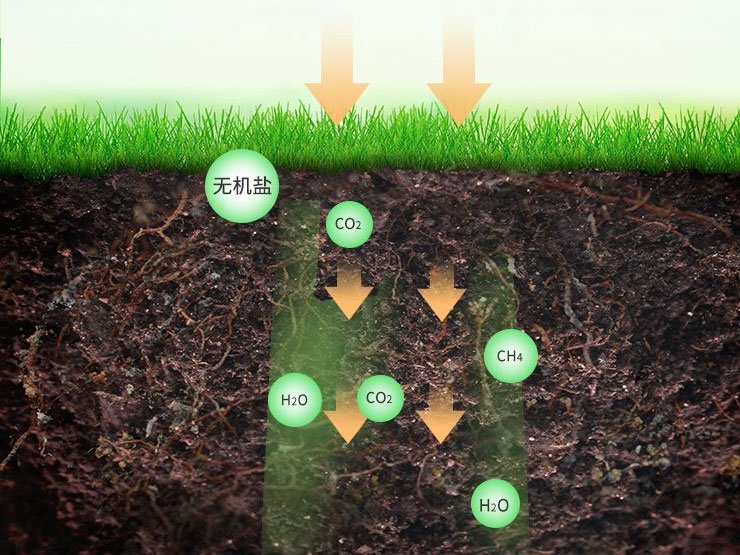
Degradation: Compostable vs. Biodegradable
Biodegradable
Time: There is no time limit for degradation. "Biodegradable" plastic bags can take hundreds of years to decompose and pollute the environment for generations.
Conditional loopholes: A material may biodegrade well in certain soils and with certain microorganisms, breaking down in the ocean or in landfills. However, in these cases, biodegradable items not only fail to decompose as expected, but also release methane, a greenhouse gas over 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide, due to their very slow decomposition rate.
Toxic residues: Products can break down into smaller fragments. Many so-called biodegradable plastics are actually regular plastics with additives added to break them down into microplastics. These toxic particles can contaminate our soil, water supplies, and food chain, causing greater harm than the original plastic.
Compostable
Decomposition: Breaks down into tiny fragments (less than 2 mm) invisible to the naked eye within 12 weeks in a composting environment.
Biodegradation: Converts at least 90% of organic carbon into carbon dioxide within 180 days. This demonstrates microbial consumption.
Leaving no toxic residues: The final compost must be tested for heavy metals and other toxic substances to ensure it is safe for growing new plants.
Supporting plant growth: The final compost must be able to support plant growth, demonstrating its beneficial, rather than harmful, impact on the ecosystem.
| Category | Biodegradable | Compostable |
|---|---|---|
| Degradation Time | No specific time limit; may take hundreds of years to decompose. | Must break down into fragments (<2 mm) within 12 weeks in a composting environment. |
| Environmental Impact | Can pollute for generations due to slow degradation. | Designed for rapid breakdown and integration into the environment. |
| Conditions Required | May only degrade under specific soil or microbial conditions. | Must meet standardized composting conditions (industrial or home compost systems). |
| Byproducts | May release methane (a potent greenhouse gas) during slow breakdown in landfills or oceans. | Converts at least 90% of organic carbon to CO₂ within 180 days, showing effective microbial breakdown. |
| Residue | Often leaves toxic microplastics; many are traditional plastics with additives. | Leaves no toxic residues; compost is tested for heavy metals and toxins. |
| Impact on Soil | Potentially harmful; contaminates soil, water, and food chains. | Final compost must support plant growth, showing its safety and environmental benefit. |
Industrial Composting vs. Home Composting
Not all composting is created equal. There are two main types of composting, and your current product is likely designed for only one of these.
Industrial Composting
Industrial composting facilities are ideal for composting. They provide the perfect conditions for compostable products to fully decompose: sustained high temperatures (55-70°C or 131-158°F), controlled humidity, and a high concentration of specific microorganisms. The vast majority of compostable food packaging, cutlery, and coffee cups are designed for these industrial facilities.
Home Composting
This is limited by environmental conditions. Temperatures are lower and fluctuate, and the balance of microorganisms varies. This system is excellent for things like fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, and yard trimmings. The downside is that it often lacks the sustained heat required to break down more complex bioplastics, such as polylactic acid (PLA), a common material used in compostable cups and cutlery.
How can you tell the difference between industrial composting and home composting?
Products certified for industrial composting may not necessarily decompose in a home compost bin. If you want to compost at home, it's important to look for products specifically certified for home composting. These products have been tested and proven to break down even in the cooler, more variable conditions of a home composting pile. The "OK compost HOME" certification is the most common and trusted standard.

What Are Some Recognized Certifications for Compostability?
| Certification | Region | Issuing Organization | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPI (Biodegradable Products Institute) | North America | BPI | Ensures the product meets ASTM D6400 or D6868 standards for industrial composting in North America. |
| Seedling Logo (European Bioplastics) | Europe | European Bioplastics | Indicates the product is industrially compostable according to EN 13432 standards. |
| OK compost INDUSTRIAL | International / Europe | TÜV Austria | Another globally respected certification based on EN 13432 for industrial composting. |
| OK compost HOME | International / Europe | TÜV Austria | Guarantees the product can decompose at low temperatures in home composting systems. |

Biodegradable vs. Compostable: Which Is Better?
Biodegradable Packaging:
- Breaks down naturally over time through microbial activity.
- The term lacks specific standards regarding decomposition timeframes and conditions.
- May leave behind residues or microplastics if not properly managed.
Compostable Packaging:
- Designed to decompose under specific conditions into non-toxic, nutrient-rich compost.
- Meets established standards (e.g., ASTM D6400, EN 13432) ensuring complete breakdown within a defined period.
- Leaves no harmful residues, enriching the soil.
How to Choose the Most Sustainable Packaging
Understand Disposal Infrastructure:
Ensure access to appropriate composting facilities if opting for compostable packaging.
Recognize that biodegradable materials may not decompose effectively in landfills.
Check for Certifications:
Look for certifications like ASTM D6400 or EN 13432 for compostable products.
Be cautious of vague "biodegradable" claims without certification.
Consider the Product's Lifecycle:
Assess the environmental impact from production to disposal.
Opt for materials that align with your sustainability goals and disposal capabilities.
Educate Consumers:
Provide clear disposal instructions to ensure proper end-of-life handling.
Transparency builds trust and promotes environmental responsibility.

Difference Between Biodegradable and Compostable Common Misconceptions
Do biodegradable products really not break down in landfills?
In most cases, the answer is yes. Landfills are merely storage facilities; without oxygen, the microorganisms needed for biodegradation are restricted, and over time, methane is produced, which is harmful to the environment.
Are all bioplastics compostable?
Absolutely not. "Bioplastics" simply means that the plastic is derived from a renewable biological source (such as corn or sugarcane), rather than petroleum. Some bioplastics, such as polylactic acid (PLA), can be composted under industrial conditions. Other bioplastics, such as bio-PET, have the same structure as fossil fuel-based plastics and are designed to be durable and recyclable, not compostable.
My city doesn't have industrial composting facilities. What should I do?
In this case, the best option is to use a reusable product (for example, a reusable coffee cup). Without a processing facility, it will likely end up in a landfill.
Are compostable products always better than recyclable ones?
This isn't always the case; it depends on the product and the system. For items that come into direct contact with food waste (such as dirty napkins or greasy pizza boxes), composting is a better option, as food scraps can contaminate the recycling stream.
For clean aluminum cans or glass bottles, recycling is a better option, as these can be efficiently recycled almost infinitely.
Conclusion
The difference between biodegradable and compostable isn't simple knowledge. Products labeled "biodegradable" often support a linear "take-make-discard" economic model. When you choose a verifiable compostable product and dispose of it properly, you participate in the circular economy.
Sources & Further Reading
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). https://www.epa.gov/
- Biodegradable Products Institute (BPI). https://bpiworld.org/
- TÜV AUSTRIA. "OK compost HOME."https://en.tuv.at/
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation. "What is a Circular Economy?" https://www.weforum.org/organizations/





